Introduction
As more people work remotely worldwide, organizations are struggling to keep their networks and data secure. Traditional security methods find it hard to adapt to the changing and spread-out nature of remote workforces. But microsegmentation offers a solution. It provides detailed control over network access and how data moves. This blog explores how microsegmentation can effectively enhance security for remote workforces, ensuring that organizations can maintain robust defenses without compromising productivity or flexibility.
Understanding Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation is a network security approach that divides a network into smaller, distinct segments or zones. This helps isolate critical assets and minimize the overall attack surface. Unlike traditional security models that use a single firewall to protect the whole network, microsegmentation applies security policies at a finer level—typically at the workload or application level. This approach allows organizations to enforce strict access controls based on user identity, role, device status, and other relevant details, regardless of user location.
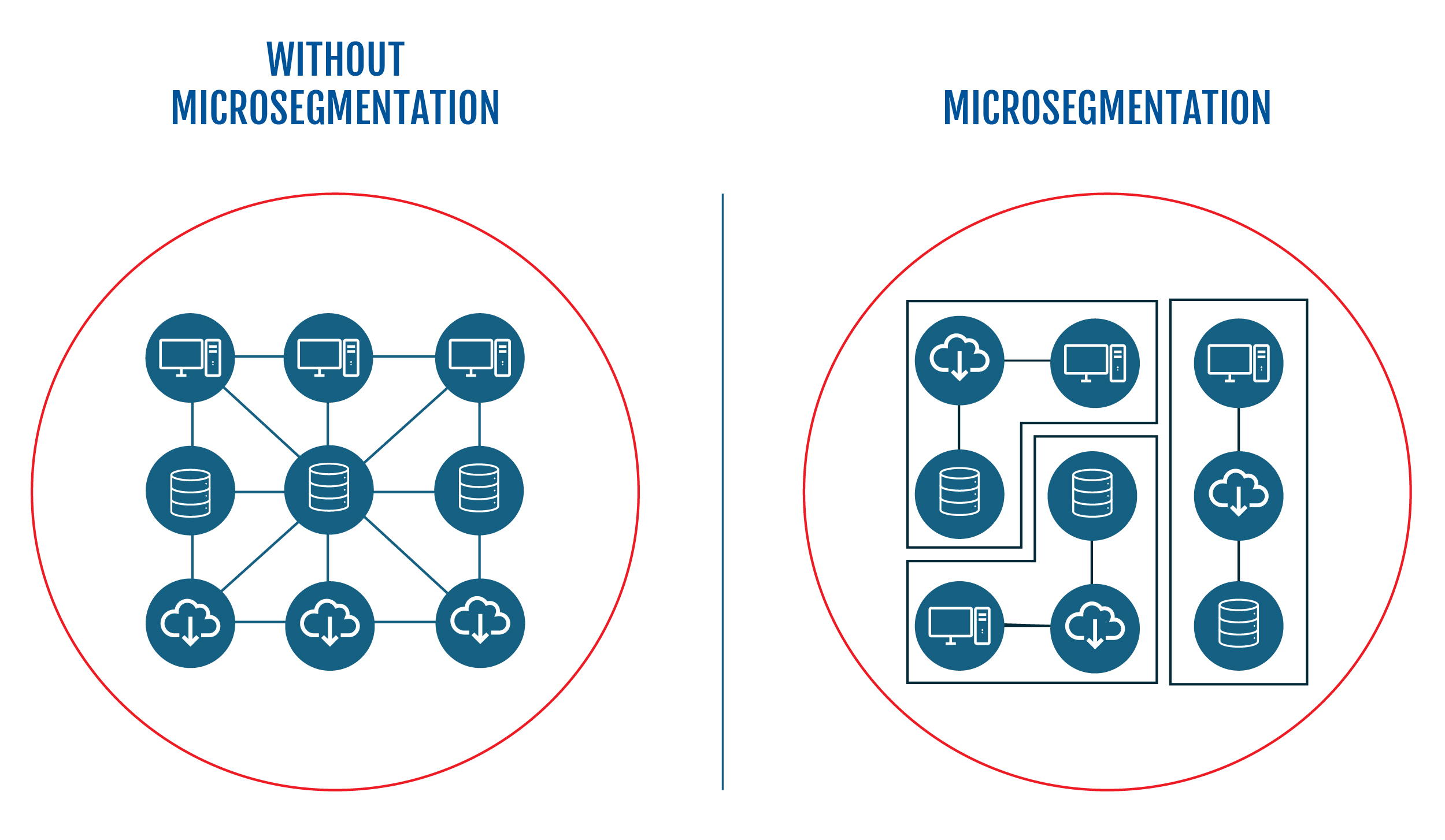
Key Security Challenges for Remote Workforces
With the rise of remote work, companies are encountering unique security challenges that traditional measures often can’t handle. These challenges can expose sensitive data and create vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit. While microsegmentation can help mitigate these risks, it’s essential to understand the specific challenges organizations encounter in securing remote workforces.
Here are some key issues:
Increased Attack Surface: Remote work allows employees to access company resources from various devices and locations, making it easier for attackers to identify weak points in security.
Endpoint Security Risks: Devices used by remote workers may not be as secure, leaving them more susceptible to malware and phishing attacks.
Data Protection: Organizations must ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data transmitted over potentially insecure networks.
Compliance Concerns: Adhering to regulatory requirements and industry standards is crucial when data is accessed and stored outside traditional corporate networks.
Authentication and Access Control: Verifying the identity of remote users and managing their access can be complex. Weak authentication methods or poorly managed access controls can lead to unauthorized access.
Network Connectivity and Reliability: Remote work heavily relies on internet connectivity. Issues like network outages, slow connections, or using unsecured public Wi-Fi can compromise security and disrupt productivity.
Monitoring and Incident Response: Tracking remote workers’ activities and responding promptly to security incidents can be challenging. Organizations need effective tools and processes to detect unusual behavior or signs of compromise in remote environments.
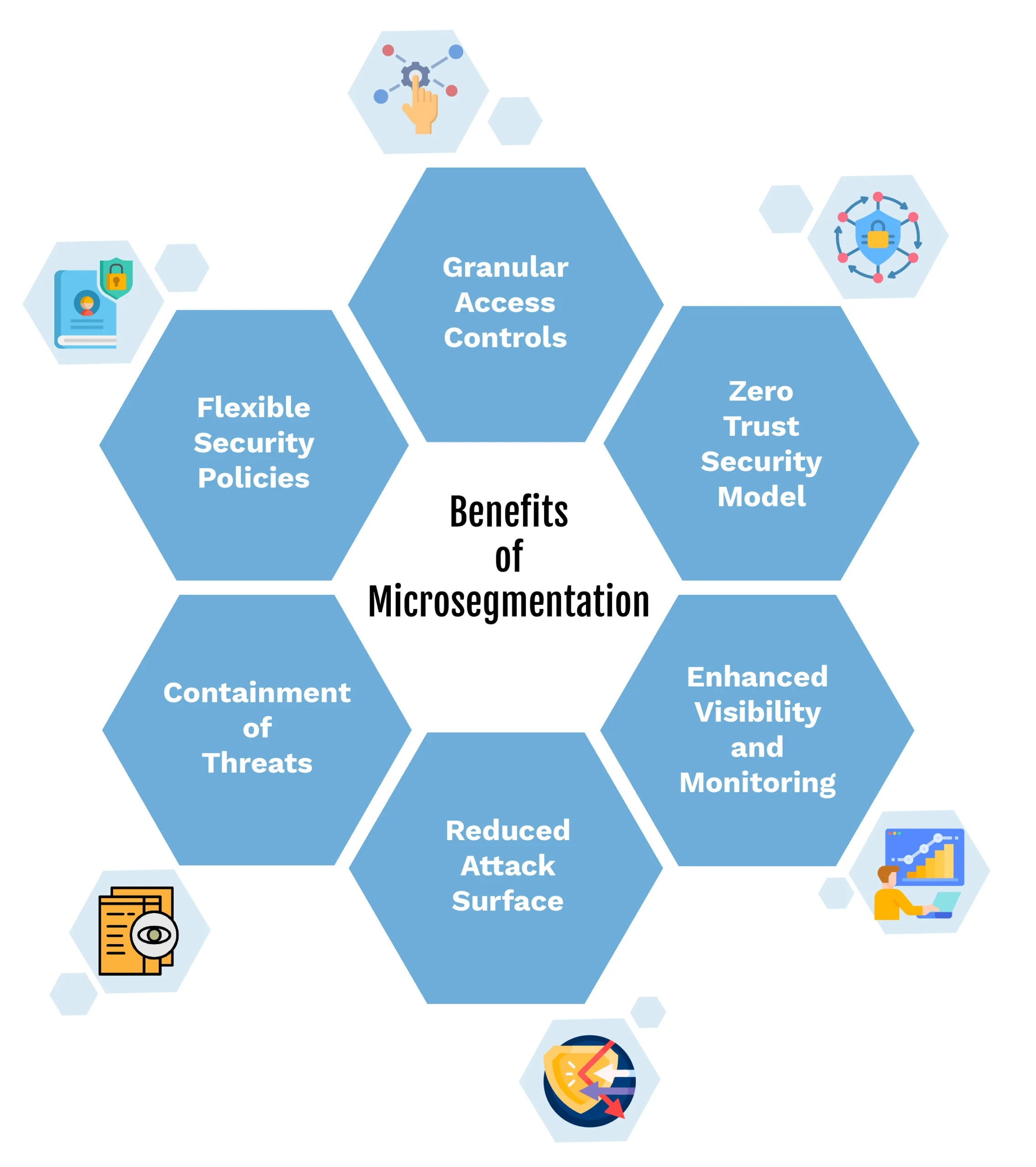
Benefits of Microsegmentation for Remote Workforces
With the rise of remote work, safeguarding networks has become more critical than ever. Microsegmentation provides an effective approach to security by dividing networks into smaller, isolated segments, making them easier to protect and manage.
This approach brings several important benefits:
- Granular Access Controls: By segmenting the network and applying policies based on user identity and device attributes, organizations can limit lateral movement and minimize the impact of a potential breach.
- Zero Trust Security Model: Microsegmentation aligns well with the Zero Trust security model by verifying every request for network access, regardless of the user’s location or network environment.
- Enhanced Visibility and Monitoring: Improved visibility into network traffic and user behavior enables immediate detection and response to security incidents.
- Improved Compliance: Microsegmentation helps organizations achieve compliance with data protection regulations by applying access control to sensitive data and monitoring data flows.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Microsegmentation splits the network into smaller parts, so if attackers get into one part, they can’t access the rest.
- Containment of Threats: If a breach occurs, microsegmentation helps limit the damage to just the affected part of the network, preventing it from spreading to the entire system.
- Identify Critical Assets and Data: It helps identify and protect important data and resources within the network.
- Flexible Security Policies: It allows organizations to apply specific security policies to different parts of the network based on their unique security requirements, ensuring tailored protection where needed.
- Scalability: Microsegmentation can easily scale with the organization’s growth and changing network environments, adapting to new devices and applications without compromising security.
- Improved Performance: By directing and prioritizing network traffic within segments, microsegmentation can enhance overall network performance and efficiency.
Microsegmentation not only enhances security by restricting access and isolating threats but also improves network performance and scalability, making it a valuable strategy for modern cybersecurity challenges.
Steps to Implement Microsegmentation for Remote Workforces
Understand Your Network: Start by thoroughly understanding your network setup. Know what devices are connected, how data moves between them, and which parts of your network are most critical to protect. This knowledge forms the basis for your microsegmentation plan.
Identify Critical Assets and Data: Identify the most critical assets and data for your organization, such as customer records, financial details, or proprietary software. Focus on these for enhanced segmentation and protection. Prioritize these for stronger segmentation and protection.
Plan Your Segmentation Strategy: Develop a clear strategy for dividing your network into smaller segments. Focus on isolating critical assets and sensitive data and define which users or devices will have access to each segment, along with strict security policies.
Define Security Policies: Create detailed security policies based on user roles, device types, and the sensitivity of the data. These policies should be adaptive, and able to adjust based on real-time security threats and changes in your network environment.
Deploy and Integrate Solutions: Implement microsegmentation solutions that seamlessly integrate with your existing network infrastructure and remote access technologies. Ensure these solutions support secure connections for remote workers without compromising usability.
Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor network traffic and security events within each segment. Use this data to optimize your microsegmentation policies over time. Stay flexible to adjust policies as your business and security needs evolve.
Challenges of Implementing Microsegmentation
Complexity in Policy Management and Enforcement: Managing multiple segmentation policies across a distributed workforce can be challenging. It’s crucial to enforce these policies consistently across different user roles, device types, and network setups. This requires strong centralized tools for managing policies and automating enforcement.
Scalability Issues: Scaling microsegmentation to accommodate more remote workers and devices accessing company resources can be difficult. Organizations need scalable solutions that can handle changes in network traffic and user access patterns dynamically, without slowing down performance or compromising security.
Balancing Security and User Experience: Balancing robust security measures with a smooth user experience is essential. Adaptive security policies that adjust based on factors like where users are and what devices they use can help avoid disruptions to productivity.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Integrating microsegmentation with existing network setups, firewalls, and security tools requires careful planning and compatibility checks. Using APIs and integration features from microsegmentation providers can make deployment and management smoother.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Meeting compliance regulations like GDPR and HIPAA while implementing microsegmentation involves protecting data and privacy. Ensuring that microsegmentation policies align with these regulations and including encryption and access controls where needed is vital.
Monitoring and Incident Response: Monitoring network traffic and responding to security incidents in a decentralized microsegmented environment can be challenging. Using thorough monitoring tools and setting up effective incident response plans are crucial for quickly detecting and addressing threats.
Future Trends in Microsegmentation
As companies improve their security practices, a few key trends are emerging in microsegmentation.
One important trend is the integration of Zero Trust architecture. This means continuously monitoring user behavior and adjusting access controls to verify identities. It helps ensure that users only have access to what they absolutely need.
Another trend is the use of automation and orchestration. By automating policy management and incident response, organizations can apply security rules consistently and respond to security incidents more quickly.
Advanced threat detection is also gaining attention. Using AI and machine learning allows for real-time analysis of network data, helping to spot unusual activities faster and respond to security threats more effectively.
These trends are helping to make microsegmentation an even stronger tool for creating secure network environments.
In conclusion, microsegmentation offers strong security for remote workforces by providing detailed access controls, improving visibility, and reducing risks. By customizing microsegmentation strategies to fit their needs, organizations can better protect their networks, data, and remote devices through effective remote device management from evolving cyber threats. As remote work continues to grow, it’s important for companies to evaluate their security measures and consider using microsegmentation to stay safe in a changing environment.