What exactly is Google Mobile Services (GMS)?
GMS stands for Google Mobile Services, and it refers to a selected array of Google proprietary applications and services that embody the company’s core values. The apps such as Chrome, Gmail, YouTube, Maps, PlayStore and many more form a part of the GMS applications.
Android devices need the GMS certification to run all the Google proprietary applications, without which, the device will not be able to operate any of these applications. Apart from that, all users expect these basic applications to function smoothly right out-of-the-box (OOTB), with no crashes or failures.

Why Android-based smart devices?
Android is Google’s open-source operating system for mobile devices. It was first introduced for smartphones and tablets, but because of its widespread success and user adoption, Android extended its support to other smart devices like wearables, automotives, and enterprises. Its open-source nature, regular updates, periodic OS optimization, and Google’s development assistance are all factors that contribute to its popularity, making it a significant platform for mobile app development services.
How is the Android Operating System related to GMS?
The Android Open Source Project (AOSP) corresponds to the Android Operating System (OS). The AOSP, which is independent of the GMS, only allows the Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) to run Android OS on their own devices. You do not need a GMS license to run Android OS on your devices; it is completely free; for example, Amazon uses Android for its Fire smartphone without any sort of agreement with Google.
To receive an Android device certification, the devices must pass several Google-designed compatibility tests and processes.
GMS License and GMS Certification
The GMS license, also known as the Mobile Application Distribution Agreement (MADA), is Google’s permission for your company to use its GMS suite of applications and services on your devices. GMS license is nontransferable and nonexclusive.
The GMS Certification confirms that the device meets Google’s performance criteria and can run Google apps successfully, allowing it to be launched in the market with GMS suite of apps and services.
Simply said, the GMS license is for your brand while the certification is for your device that you manufacture.
GMS Certification for Android Pie
Since 1st March, 2019, Google has only been considering the devices with Android Pie’s latest version for the GMS certification, for an improved user experience.
Thus, the devices with the older OS versions like Oreo and lower cannot be GMS certified, but as non-GMS devices, which implies that the mobile services applications must be removed from them.
Applying for a GMS License
For the GMS license, all you have to do is to fill up this contact form.
from the Android’s website and apply for a license in advance of your planned roll-out. This form asks for the information that you need to provide to acquire a GMS license. Fill in the details such as the device form factor (phone, wearable, TV, etc.), brand and company information, previous experience with android devices, number of devices expected to be built, countries and channel of selling the device, and the device’s Android OS version, etc.
Once the information is submitted, Google will analyze your request, your company, and its products. If Google determines that the OEM/Company/Distributor that submitted the application is qualified enough to receive a GMS license, they will contact you. Google may take a long time to respond. Upon successful review by Google, the company gets MADA ̶ the GMS license.
Android Product Life Cycle with GMS Certification
If you are an OEM and want to launch your Android device with the GMS suite of apps and services, then your device must follow the below-mentioned development cycle.
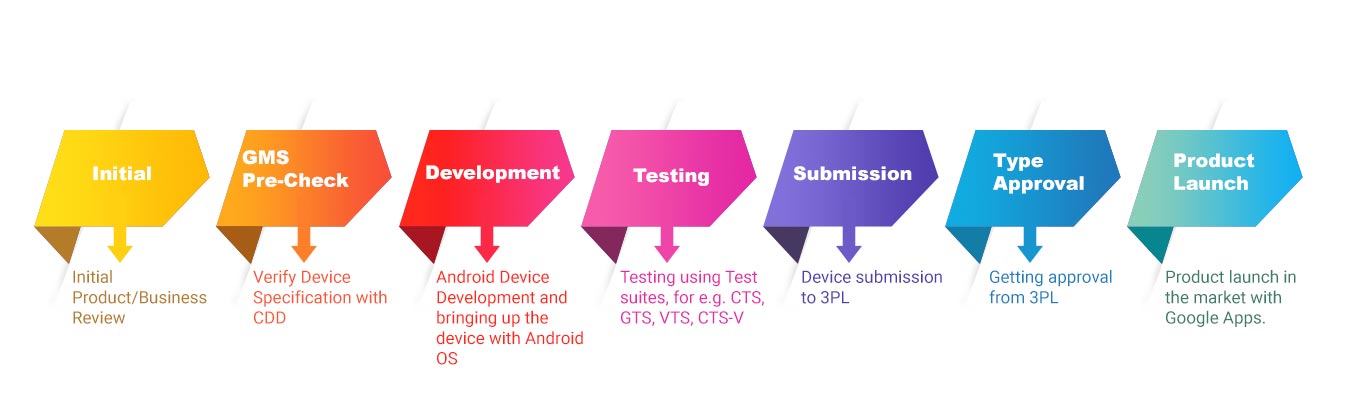
Initial
Normally, the product design starts with the conceptualization and/or the proof-of-concept phase. GMS and the related activities must be considered during the project’s initial phase as the GMS certification is not a feature to be parked for a later product design phase. The product features, mechanical form factor, budget for the GMS activities, etc. should be considered during the initial product lifecycle phase.
GMS Pre-Check
If an Android device is to be GMS certified, it must fulfill all the requirements listed in the Compatibility Definition Document (CDD). This document lists the requirements that the devices must meet to be compatible with Android’s latest version. To be considered compatible with Android, device implementations must meet the standards outlined in this compatibility definition, including any publications referenced. For each release of the Android platform, a detailed CDD is provided. This document defines the Android device requirements for various device categories such as handheld, television, automotive, watch, and tablet, etc.
More information can be found by following this link.
Product software, hardware, and mechanical requirements must comply with the CDD provisions. To avoid any future questions, it is a good idea to have the product’s hardware, software, and mechanical specifications reviewed by the GMS certification experts.
Development
The device development cycle can begin once the device specifications meet all the CDD’s standards and Google approves both the mechanical and the device specifications.
Testing
Once the product has ported to Android, it is time to run Google’s pre-defined test suites that examine the Android OS and the Google Apps for security, performance, and compatibility.
The automated test suite follows the below-mentioned workflow:
The automated test suite tool is installed on the host PC and the device to be tested is connected to the host PC via the Android Debug Bridge (ADB). The test suite tools run a set of test cases on the device and record the results. After completion of all the test cases, it generates the test reports. The Compatibility Test Suite (CTS) example is shown below:
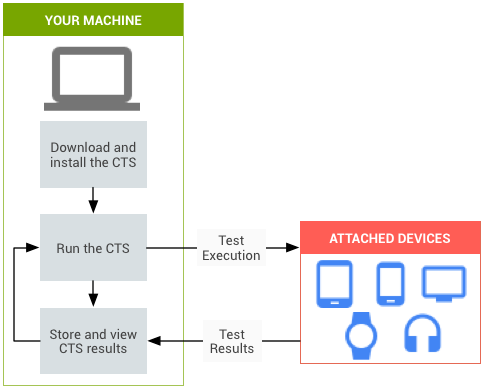
Where as in the manual test suite, the Android applications are installed and the device is tested manually as directed by the application. CTS, Google Mobile Services Test Suite (GTS), Vendor Test Suite (VTS) are automated test suites and CTS-V is a manual test suite. These tools are explained below:
Compatibility Test Suite (CTS)
The Compatibility Test Suite (CTS) evaluates the compatibility of Android OS with the hardware by running more than 300K unit test cases. Compatibility test cases cover different areas such as signature tests, platform API tests, Dalvik tests, platform data model, platform intents, platform permissions, and platform resources, etc. Once the CTS tests are cleared, the manual test tool Compatibility Test Suite Verifier (CTS-V) is used to validate it.
Compatibility Test Suite Verifier (CTS-V)
The Compatibility Test Suite Verifier (CTS-V) is a CTS supplement. The CTS verifier provides tests for the Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and functions that cannot be tested on a stationary device without manual input (e.g. camera, audio quality, and accelerometer, etc.).
The CTS verifier is a tool for manual testing and includes the following software components:
- The CTS verifier app that is executed on the device and collects the results.
- The executable(s) or script(s) that are executed on the desktop machine to provide data or additional control for some test cases in the CTS verifier app.
Vendor Test Suite and CTS-on-GSI
The Vendor Test Suite (VTS) automates the HAL and OS kernel testing. The testing is done with the Generic System Image (GSI). A GSI is a system image with adjusted configurations for Android devices. It is a pure unmodified Android implementation with the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) code that can operate successfully on any Android device running Android 8.1 or higher. GSIs are used for conducting VTS and CTS-on-GSI tests. The system image of an Android device is replaced with a GSI, then, tested with the VTS test cases and the CTS-on-GSI test cases. The CTS-on-GSI tests are the subset of the CTS tests.
GMS Test Suite
The GMS test suite is the Google proprietary test suite which examines the compatibility of Google Apps with the Android device. In addition to that, the GMS test suites also perform various security related tests to verify that the user’s data on the device is secure.
Submission
When all the test suites pass with zero failures and the device is ready, it is sent to a 3PL for certification. Before submitting the device for certification, it must have the latest security patches installed.
The Role of 3PL in GMS
3PL or Third Party Labs are Google authorized labs that provide the GMS certification. They perform independent testing on behalf of Google, across a vast array of features and performance requirements.
The 3PL makes sure that the device and the OEM respect the CDD, perform a series of tests with different test suites (CTS, CTS-V, VTS, GTS), and validate the Android-based product and check the compatibility for the GMS certification. 3PL certifies the device on successful compliance in all the expected aspects in around four weeks.
Approval
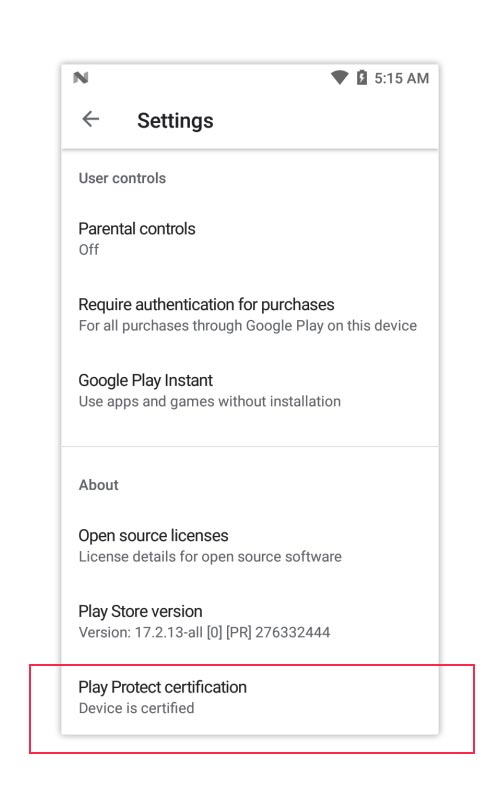
Once the device is GMS certified, its fingerprint will be registered with Google and the same will be seen in the Google Play store setting menu underplay protect certification tab as shown in the below image.
Product Launch
After the device gets the GMS certification, Google approves it for the market launch with all the Google apps and services.
How eInfochips can help
eInfochips has been providing services to OEMs related to the GMS certification for long. Once the customer obtains MADA from Google, eInfochips can help in providing support for the GMS certification in the following ways:
- Involve in the initiation phase to define the product’s hardware, software, and the mechanical specifications.
- Identify the risks in the overall program w.r.t. the GMS certification and provide risk mitigation plan for the same.
- Prepare the budget and the timelines to carry out activities related to the GMS certification.
- Undertake GMS pre-check to review the product specifications for the GMS certification compliance.
- Software/Hardware design and development of the Android product with CDD compliance.
- Run various tests like CTS and other; fix all the issues to meet all the GMS compliance aspects.
- Apply and fix all the security upgrades before submitting the device for certification.
- Submit the device to the 3PL for certification and provide support for the queries reported by 3PL during the certification process.
Are you interested in obtaining the GMS license for your planned Android device? Contact us.
Update: This article was updated by Ronak Patel













