The Oxford dictionary defines evolution as a gradual development of something. The world became what we see today due to constant evolution. As everything around us changed from generation to generation, the mobile wireless network also evolved from 1G (first generation) to 5G (fifth generation).
The first generation (1G) delivered analog voice, which had low capacity, poor voice links, and no security. Then came the second generation (2G) which introduced digital voice based on GSM technology, opened the world to text and picture messages. The third generation (3G) brought mobile data-video chats and other video access were enabled. With increased demand of data and quality a much faster 4G technology emerged. The fourth generation (4G) mobile technology offers high voice quality, improved data transfer speed with reduced latency.
The much-awaited fifth-generation (5G) wireless network of mobile internet connectivity is developed to provide faster and reliable connections to mobile devices. 5G network is expected to give a huge rise in areas of mobility, Virtual Reality, and the Internet of Things. 5G will require a massive infrastructure to carry large amounts of data that would provide a smarter, safer, and faster network to enable a connected world of people and devices.
5G and the World
5G is the next big thing in wireless technology. With 5 times faster than 4G LTE, when fully implemented it will be a real big thing. 5G is rolling out rapidly in the world. Telecom providers around the world are competing in enabling & launching 5G. Full-scale implementation of 5G around the world is yet to be a reality, though there are more than a few 5G networks already up and running around the world. When it comes to the question of who launched the first 5G network, the answer will depend on whom the question is asked.
5th generation network was initially launched by South Korea in April 2019, according to a report published by Reuters. However, this report was challenged by top US telecom provider AT&T as they announced their 5G launch in 12 cities by early 2019 in a report that was published at the year end of 2018. And in January 2019 they provided NETGEAR Nighthawk 5G Mobile Hotspots.
Similar claim was made by Verizon Communications Inc. The vigor with which various telecommunication service providers claim themselves to be the first to launch 5G shows the competition will remain high for the foreseeable future.
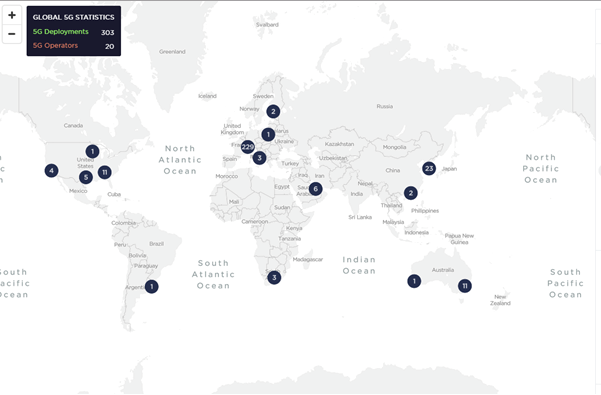
The rate at which the world is moving to 5G is highly impressive. The growth of commercial availability of 5G Network can be seen in the interactive map from Ookla. In May 2019, the map showed 303 5G networks, which had raised to 1249 by November 2019, and by December 2019 the commercial availability of 5G has been raised to 6406.

5G and India
Indian telecom network is 2nd largest in the world in terms of telephone connections, with 1183.41 million connections. The tele-density (number of telephones per 100 people) is an Indicator of telecom penetration, and tele-density in India has increased phenomenally at 90.10 %( 2019) from 36.98% (2009) in last 10 years.
The telecom market can be segmented as wireless, wirelines, and internet services. India’s wireless voice and data services have exhibited phenomenal growth. 98.17% share of the total subscriber base are wireless telephone connections.
Wireless data subscription in India includes 2G, 3G, and 4G GSM data subscribers and CDMA data, subscribers. By 2020, a high rise in subscribers for wireless data networks is expected by TRAI. Total number of wireless telephone subscribers in India was 1176.00 million at the year ending 2018, out of which more than 49 % i.e., 578.2 million are wireless data subscribers. This was 36% in 2017. The below data shows the growth of wireless subscribers and wireless data subscribers in India from 2014 to 2018.

Since the launch of 4G technology in India in 2016, the volume of wireless data usage has increased. In 2016 the data usage was 4642 million GB which increased to 20,092 by end of 2017 and further increased to 46,404 by 2018 December.
In the year 2018 86.85% of wireless data was contributed by 4G (LTE) technology and the share of 2G, 3G, and CDMA data usage has become just nominal. More than 100 thousand million GB of data usage is expected in India by 2020. To support the year by year increase in wireless data usage 5G will be beneficial.
As telecom operators around the world are focusing on moving their LTE networks to 5G, Indian Telecoms are also working for the same. In September 2019, the Indian Union Minister for Telecom, Ravi Shankar Prasad said the 5G spectrum auction will be conducted in 2019 end or early 2020.
Historically telecom service providers around the world benefited from fixed line connectivity (telephone line using copper or optical fiber) as they could offer a broadband using the same established fixed line network. However, in India, the penetration of the fixed line network is very minimal compared to most of the developed countries. Hence the telecom sector in India could never provide multiple services using the same infrastructure, this causes high operational cost, and challenges for service providers.
According to a study from cellular operations associations of India, the current average download speed in India is 512kbps compared to other nations having greater than 100Mbps speed. Wireless technology in India can offer higher bandwidth and majority prefers wireless networks than fixed line. Also, the cost of laying fibers in different states of India may have a huge difference due to various taxes imposed by the state Governments. Lack of centralized policies and huge fluctuations in duty on telecom equipment put telecom service providers in the back foot. India is still struggling to use the full potential of 4G, only around 25% of towers in India are connected with a fibre network. However, it is more than 75% in developed countries. To adapt to 5G network, India requires more towers and very high speed connectivity between the towers.
5G Spectrum in India
Most of the world had already allocated 5G spectrum and full-fledged trials are in progress. The 5G spectrum allocation In India is not completed yet. One of the reasons 5G spectrum auction is getting delayed in India is the affordability. Majority of telecom service providers in India have reported financial loss or are in verge of announcing bankruptcy in current state bidders in an auction will be less. Even after spectrum auctions are announced and providers are ready to adapt to 5G still there is a challenge of not having inexpensive mobile phones with 5G support to enable revenue from the engagement. Even though it is a challenging situation for mobile services providers in India the need of emerging technology is being appreciated. And the Government is taking initiatives to arrange spectrum launch within next financial year.
The huge increase in subscribers and data usage shows the demand for improved telecom technology in India. The historical challenges in adapting to new technologies and costs involved in enabling the 5G network will reduce the pace of 5G rollout in India. However, Investors around the world finds potential in the Indian mobile consumer market. As a result Indian telecom service providers might overcome this hurdle sooner than expected. Qualcomm® has already designed many flagship 5G solutions based on Snapdragon™ platforms.
eInfochips provides a wide range of services to the telecommunication industry, including solutions based on 4G and 5G to help organizations build highly-customized solutions. eInfochips has an intricate understanding of different platforms and 25 years of end to end product development experience. For more information on implementing 4G and 5G based solutions please contact us today.
References
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/kevinmurnane/2019/05/15/ookla-launches-an-interactive-map-showing-all-the-5g-networks-in-the-world/#b3b0e6177a08
- https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2019/apr/04/us-dismisses-south-koreas-launch-of-world-first-5g-network-as-stunt
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-telecoms-5g/who-was-first-to-launch-5g-depends-who-you-ask-idUSKCN1RH1V1
- https://www.ericsson.com/en/cases/2019/swisscom-has-switched-on-5g
- https://www.speedtest.net/ookla-5g-map
- https://about.att.com/story/2019/2019_and_beyond.html
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/telecom/telecom-news/5g-spectrum-auction-by-year-end-or-early-2020-ravi-shankar-prasad/articleshow/71117477.cms?from=mdr
- http://dot.gov.in/












