As the world becomes more digital and cyber-attacks become more prevalent, it is critical to ensure that systems, software, and applications are secure. Threat modeling arises as a vital step in bolstering defenses against possible vulnerabilities and attacks. Through the systematic identification, evaluation, and mitigation of risks, threat modeling helps enhance security across various domains. In this blog, we delve into the details of threat modeling, its types, the process, its integration into the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC), its importance, and available tools and resources.
Threat modeling involves a methodical process of pinpointing and ranking potential threats and vulnerabilities within systems or applications. At its core, it involves analyzing the system’s architecture, components, and functionalities to anticipate potential cybersecurity attack vectors and mitigate them proactively.
Threat Modeling Approaches STRIDE, DREAD, and Attack Trees
STRIDE: Stride provides a framework for categorizing different types of threats based on their characteristics. This enables organizations to systematically assess risks across various dimensions.
DREAD: The acronym stands for Damage, Productivity, Availability, User Impact, and Discovery. The model helps prioritize threats by assigning scores to each metric so organizations can focus efforts on higher-risk areas.
Attack Trees: Attack trees graphically represent potential attack situations, depicting the various steps a malicious actor might take to compromise a system or exploit a vulnerability. By visualizing attack paths and dependencies, organizations can devise countermeasures to thwart potential threats.
The Threat Modeling Process Includes
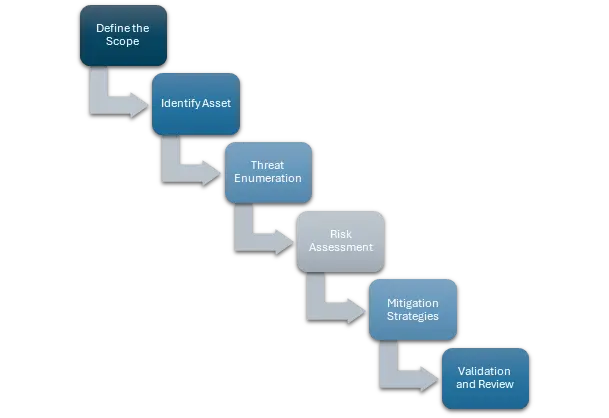
- Define the Scope: Start the threat modeling exercise by explicitly specifying the boundaries, encompassing the targeted system or application, its features and capabilities.
- Identify Assets and Entry Points: Identify critical assets, such as sensitive data or key functionalities, and determine potential entry points through which attackers could gain unauthorized access.
- Threat Enumeration: Enumerate potential threats and vulnerabilities, leveraging techniques like brainstorming, checklists, or threat libraries to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- Risk Management: Determine the probability and potential impact of each risk the usage of methodologies like STRIDE or DREAD, prioritizing excessive-chance regions for similarly evaluation and mitigation.
- Mitigation Strategies: Devise mitigation strategies to address identified risks, including architectural changes, security controls, or process improvements aimed at reducing vulnerabilities and enhancing resilience.
- Validation and Review: Validate the effectiveness of mitigation measures through testing, peer review, or simulations, iteratively refining the threat model based on feedback and insights gained.
Integrating Threat Modeling into the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC)
Incorporating the threat modeling process into the software development life cycle (SDLC) is essential. The system ensures it addresses security concerns and potential threats at each phase of development. Threat modeling helps organizations protect themselves from security breaches and high costs. It does this by finding and reducing security risks early in the development process, before problems happen.
This practice offers numerous advantages across various domains:
- Proactive Risk Management: By precisely pinpointing potential threats and vulnerabilities from the outset of development, organizations can strategically manage risks. This proactive approach facilitates the implementation of targeted countermeasures to preemptively address potential exploits before they can be weaponized, thus strengthening the overall security posture.
- Cost Savings: Addressing security concerns during the initial stages of development proves to be significantly more cost-effective than rectifying breaches or vulnerabilities post-deployment. Fixing security problems after they happen, including costs from lawsuits, damaged reputation, and lost business, is much more expensive than putting proper security measures in place from the beginning.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Adhering to stringent regulatory frameworks and industry standards is imperative for organizations to maintain trust and credibility. Threat modeling facilitates compliance by systematically assessing security risks and aligning security practices with regulatory mandates. This ensures that organizations not only fulfill but surpass the specified security requirements, thereby instilling confidence among stakeholders.
For instance, frameworks such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) mandate robust security measures to safeguard sensitive data. Integrating threat modeling enables organizations to identify potential data breaches and implement appropriate safeguards to comply with these regulations.
- Enhanced Resilience: Through systematic analysis and mitigation of risks, organizations can fortify the resilience of their systems and applications. By anticipating and addressing potential vulnerabilities, organizations decrease the likelihood and severity of security incidents, thus enhancing business continuity and reducing operational disruptions. Furthermore, threat modeling facilitates the identification of critical dependencies and contingency plans, enabling organizations to swiftly respond to security incidents and mitigate their consequences. Taking a proactive stance not only reduces disruptions to business operations but also strengthens resilience against ever-changing threats.
Several threat modeling tools and resources are available to facilitate the threat modeling process, including:
- Microsoft Threat Modeling Tool: A free tool designed to help organizations create threat models and analyze potential security threats and vulnerabilities.
- OWASP Threat Dragon: An open-source threat modeling tool that allows teams to create and collaborate on threat models using a visual interface.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Provides guidance and best practices for managing cybersecurity risks, including threat modeling methodologies and techniques.
Conclusion
Threat modeling is vital for enhancing security. It involves systematically identifying, evaluating, and mitigating potential threats and vulnerabilities. By being proactive and integrating threat modeling into their processes, organizations can strengthen their defenses against cyber threats. This helps protect their assets, data, and reputation.
The right tools, methodologies, and expertise enable organizations to leverage threat modeling effectively. This allows them to stay ahead of evolving security challenges. In today’s increasingly interconnected and digital world, threat modeling empowers organizations to tackle security risks proactively.